Welcome to ScamPy’s documentation!¶

A Python interface for Sub-halo Clustering and Abundance Matching¶
ScamPy is a highly-optimized and flexible library for “painting” an observed population of cosmological objects on top of the DM-halo/subhalo hierarchy obtained from DM-only simulations. The method used combines the classical Halo Occupation Distribution (HOD) with the sub-halo abundance matching (SHAM), the sinergy of the two processes is dubbed Sub-halo clustering and abundance matching (SCAM). The procedure itself is quite easy since it only requires to apply the two methods in sequence:
by applying the HOD scheme, the host sub-haloes are selected;
the SHAM algorithm associates to each sub-halo an observable property of choice.
What can be achieved¶
Here is an animation obtained by running ScamPy on the halo/subhalo catalogues of 42 different snapshots, from redshift z=8 to redshift z=0, of the same \(64 Mpc/h\) DM-only N-body simulation. The simulation has been obtained with the non-public code GADGET-3, following the evolution of \(512^3\) DM particles. For each different redshift we have fixed the parameters values for the HOD and matched the UV-luminosity function of star-forming galaxies.
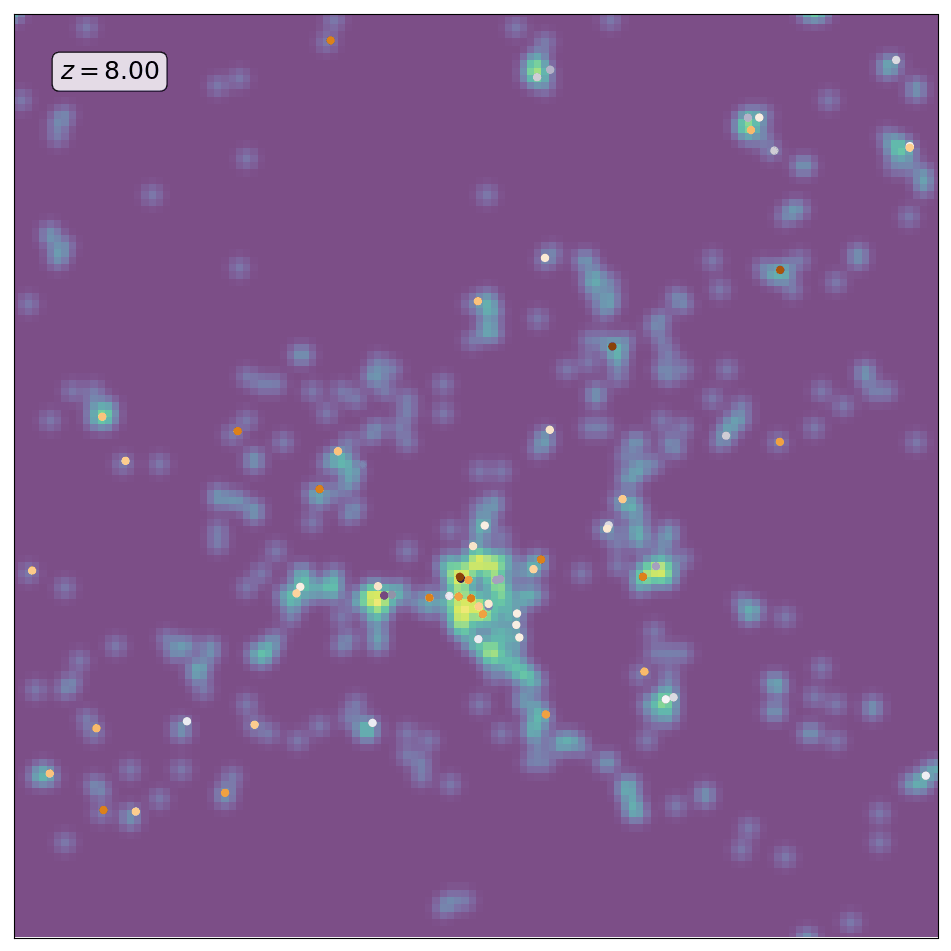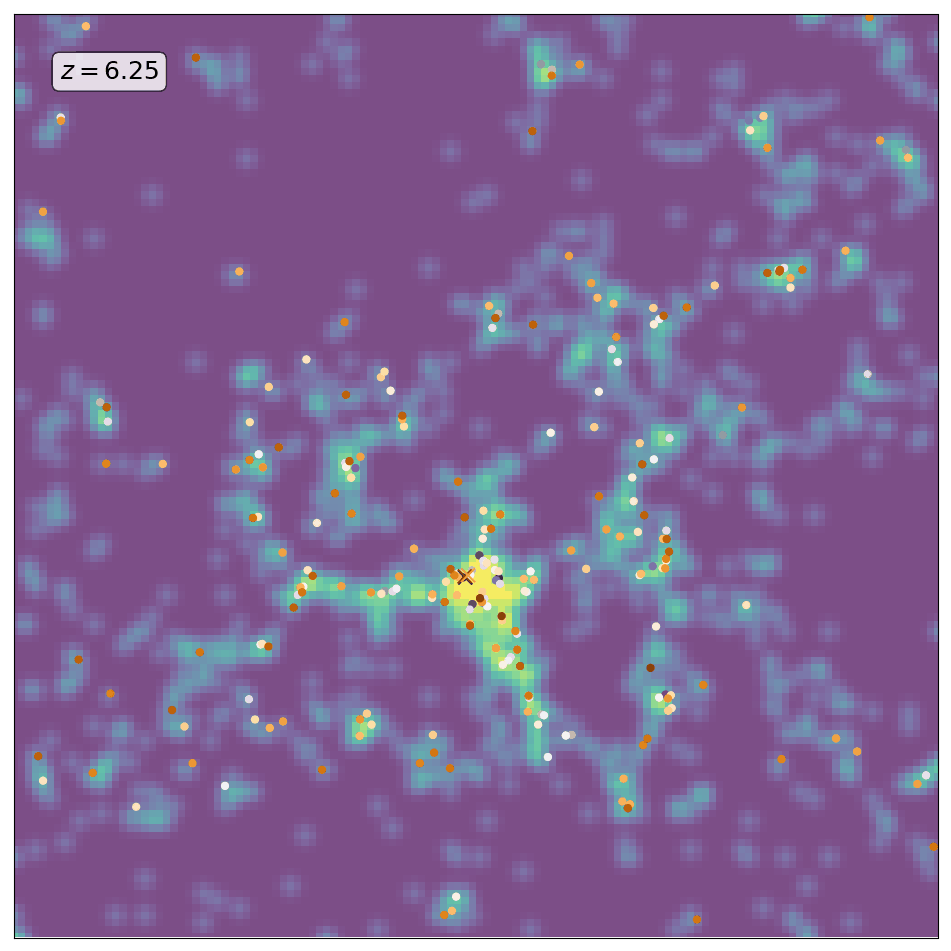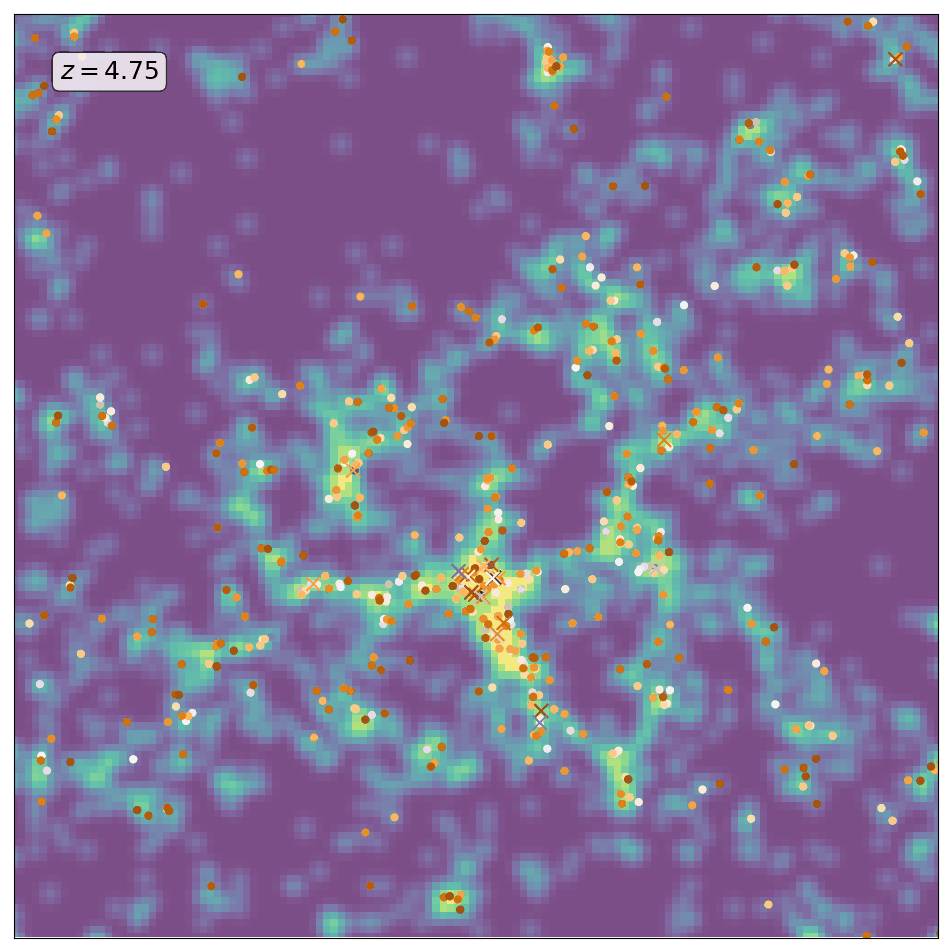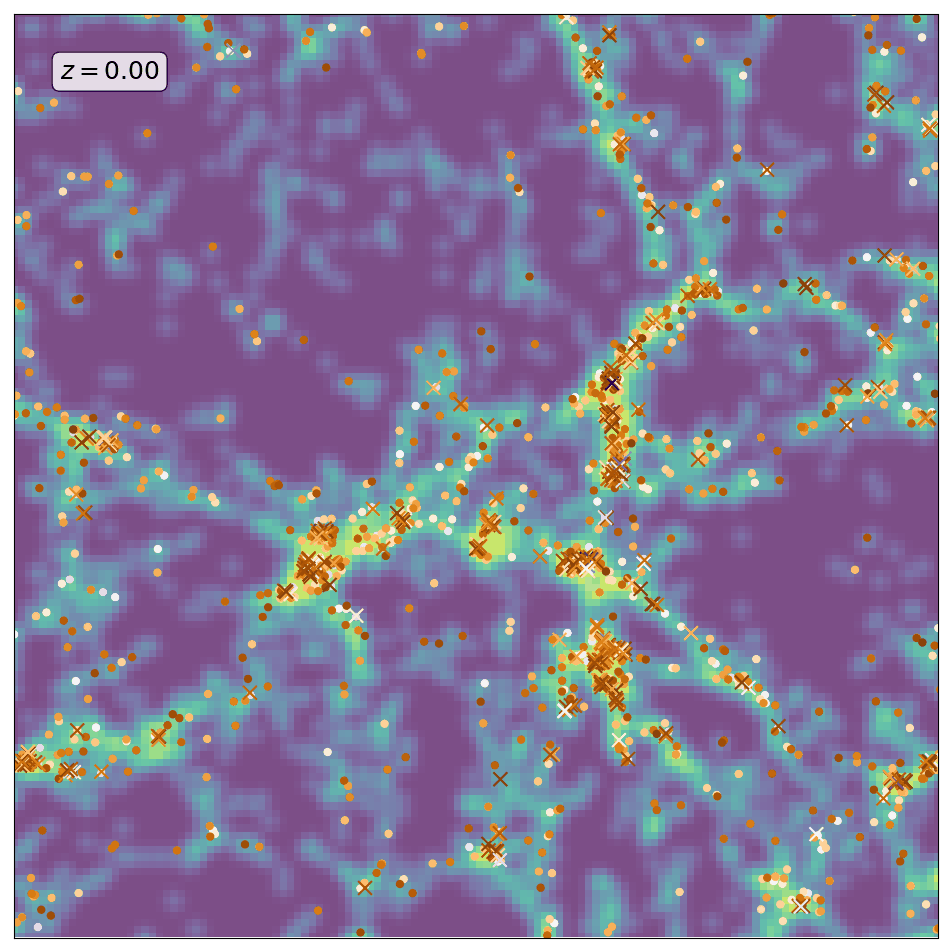
The background color-code shows the underlying DM-density field computed by smoothing the contribution of DM-particles in a 10 Mpc/h thick slice of the simulation. The markers locate the positions of the mock galaxies generated with ScamPy. Circles mark the position of the central galaxies while crosses mark the position of satellite galaxies. The marker color represents lower to higher luminosity going from brighter to darker.
Basic Usage¶
If you wanted to populate a DM catalogue with galaxies with given luminosity, you would do something like:
# read the sub-halo catalogue from a file
from scampy import catalogue
cat = catalogue.catalogue()
cat.read_hierarchy_from_gadget( "/path/to/input_directory/subhalo_tab_snap" )
volume = 512.**3 # for a box with side-lenght = 512 Mpc/h
# build an object of type occupation probability with given parameters
from scampy import occupation_p
ocp = occupation_p.tinker10_p( Amin = 1.e+14,
siglogA = 0.5,
Asat = 1.e+15,
alpsat = 1. )
# populate the catalogue
galaxies = cat.populate( ocp, extract = True )
# define a Schechter-like luminosity function
import numpy as np
def schechter ( mag ) :
alpha = -1.07
norm = 1.6e-2
mstar = -19.7 + 5. * np.log10( 5. )
lum = - 0.4 * ( mag - mstar )
return 0.4 * np.log( 10 ) * norm * 10**( - 0.07 * lum ) * np.exp( - 10**lum )
# call the sub-halo abundance matching routine:
from scampy import abundance_matching
galaxies = abundance_matching.abundance_matching( galaxies, schechter, factM = 1. / volume )
The galaxies array contains the output mock-galaxies.
Installation guide¶
Installation of ScamPy is dealt by the Meson Build System.
Each module of the API is built by a specific meson.build script.
You can decide to install it either in
- developer-mode, with shared libraries for the C/C++ sectors and headers organized in the
POSIX directory structure (libraries in
lib, headers ininclude, python package inlib/pythonX.Y/site-packages)
package-mode, with the C++ sector compiled into static libraries within an internal sub-module of the package and C-wrapping compiled dynamically along with the former. This is what you would obtain bypip-installing from the root directory of the project.
developer-mode Install¶
From the root directory of this repository run
meson build_dir --prefix /path/to/install_directory
meson install -C build_dir
If no --prefix is specified the library will be installed in the system default prefix directory (usually /usr/local).
package-mode Install¶
From the root directory of this repository either run
meson build_dir --prefix /path/to/install_directory -Dfull-build=false
meson install -C build_dir
or run
In the latter case the standard path for the python installation directory will be used.
Meson options¶
full-build: boolean, enables/disables the full build installation.enable-doc: boolean, enables/disables building of the documentation. If enabled, docs will appear in the$PREFIX/share/mandirectoryenable-test: boolean, enables/disables testing (to run tests after having compiled the project runmeson test -C build_dirfrom the root directory of this repository)
Pre-requisites¶
For building:
meson<0.57build system toolninja
can both be installed either via conda install or with pip install
Warning
The current latest version of meson (i.e. 0.57.2) does not always support compiling heritage fortran programs
(typically an error of type UnicodeDecodeError is raised).
If the external library FFTLog (see below) is not already installed in your system (and visible to the linker),
the installation process will try to download and compile it with ninja.
If your meson version is superior to 0.56.2 this will cause a failure in the installation process.
The quickest fix is to downgrade your build system tool to meson<=0.56.2.
Dependencies of the library:
GNU Scientific Library version 2 or greater (GSL link);
FFTLog (FFTLog link).
While GSL has to be already installed in the system, if FFTLog is not present Meson will authomatically download it along with a patch we have developed, both will be installed in the subprojects directory of the repository.
Dependencies for building the documentation locally:
Doxygen
Sphynx (with breathe, autodoc and rtd_theme extensions)
Note
A YAML file containing the specs for building a conda environment with all the dependencies needed to build the docs is available at doc_environment.yml
Dependencies for enabling testing:
Google Test (is authomatically installed by Meson)
Contents:
Tutorials